Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (23): 3707-3714.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.23.017
Previous Articles Next Articles
Phytohaemagglutinin stimulates the proliferation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells and expression of secretory cytokines
Wang Ding, Song Bing, Zhong Xuan, Sun Xiao-fang, Fan Yong
- Key Laboratory for Major Obstetric Diseases of Guangdong Province, Key Laboratory of Reproduction and Hereditary of the Universities in Guangdong Province, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510150, Guangdong Province, China
-
Revised:2014-04-02Online:2014-06-04Published:2014-06-04 -
Contact:Fan Yong, M.D., Associate chief technician, Master’s supervisor, Key Laboratory for Major Obstetric Diseases of Guangdong Province, Key Laboratory of Reproduction and Hereditary of the Universities in Guangdong Province, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510150, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Wang Ding, M.D., Assistant researcher, Key Laboratory for Major Obstetric Diseases of Guangdong Province, Key Laboratory of Reproduction and Hereditary of the Universities in Guangdong Province, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510150, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81202604, 31171229, U1132005; the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, No. S2013040012649; the Educational Foundation of Guangdong Province, No. 2013KJCX0149; the Plan of Science and Information Technology Bureau of Guangzhou City, No. 2011y-00038-1; the Ph.D. Programs Foundation of Ministry of Education of China, No. B2012169
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Ding, Song Bing, Zhong Xuan, Sun Xiao-fang, Fan Yong . Phytohaemagglutinin stimulates the proliferation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells and expression of secretory cytokines[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(23): 3707-3714.
share this article
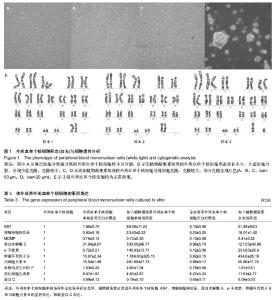
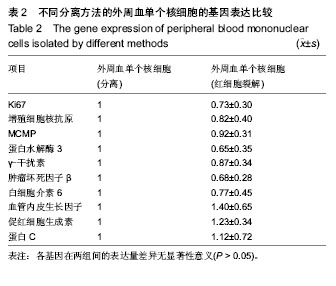
以淋巴细胞分离液所得外周血单个核细胞的各基因表达量为1,计算裂解红细胞所得外周血单个核细胞的基因表达量。统计学分析发现两者之间差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。 2.2 外周血单个核细胞体外培养形态学观察 对淋巴细胞分离液分离的单个核细胞进行光镜观察发现细胞较小,细胞分散较好,没有细胞聚集现象。在无植物凝集素的培养基中培养60 h,仍有大量细胞分散,同时出现少量细胞克隆,克隆较小;在含植物凝集素的培养基中培养60 h,细胞形态相近,部分细胞悬浮于培养基中,有少量细胞克隆出现,细胞克隆明显大于无植物凝集素培养所现克隆,高倍光镜观察,发现部分克隆呈现红色(图1)。因全血培养,红细胞较多,无法光镜观察。 细胞遗传分析显示,3个样本均为正常核型。培养前分离外周血单个核细胞组和不加入植物凝集素培养组无分裂相,加入植物凝集素组可见分裂相。 2.3 植物凝集素促进外周血单个核细胞增殖以及凋亡 检测细胞培养以及培养过程中添加植物凝集素,引起的外周血单个核细胞的Ki67、增殖细胞核抗原、MCMP和蛋白水解酶3基因表达的变化(表3)。"
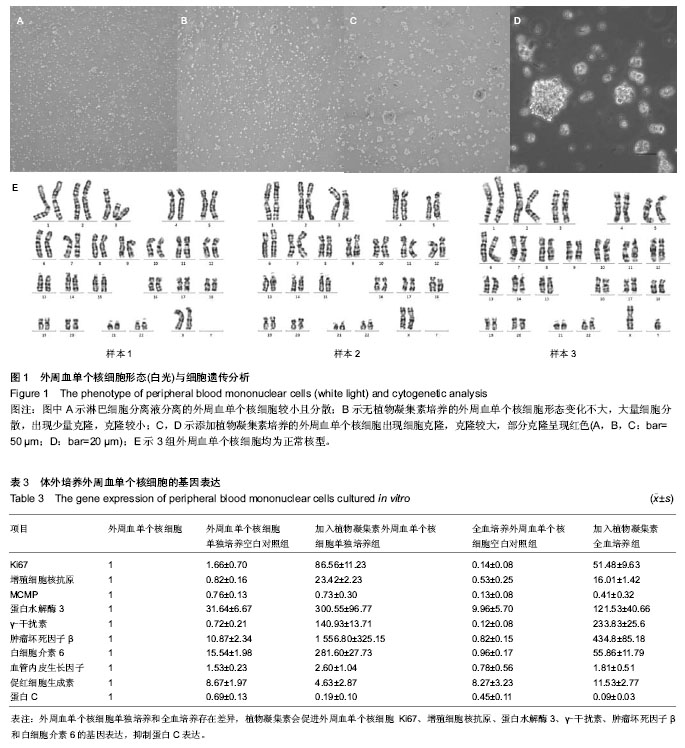

相对培养前的外周血单个核细胞:①在不添加植物凝集素组中,外周血单个核细胞培养组蛋白水解酶3的表达明显上调;全血培养组MCMP明显下降,蛋白水解酶3的表达明显上调(P < 0.05)。②在添加植物凝集素组中,外周血单个核细胞培养和全血培养组结果一致,Ki67、增殖细胞核抗原和蛋白水解酶3明显上调(P < 0.05),MCMP变化不明显(P > 0.05)。相对不添加植物凝集素组,添加植物凝集素的培养中,外周血单个核细胞培养和全血培养组结果一致,Ki67、增殖细胞核抗原和蛋白水解酶3明显上调(P < 0.05),MCMP变化不明显(P > 0.05)。相对外周血单个核细胞培养,全血培养中蛋白水解酶3明显下调(P < 0.05),不添加植物凝集素组的Ki67和MCMP明显下调(P < 0.05),其他基因表达变化不明显(P > 0.05),见图2。"
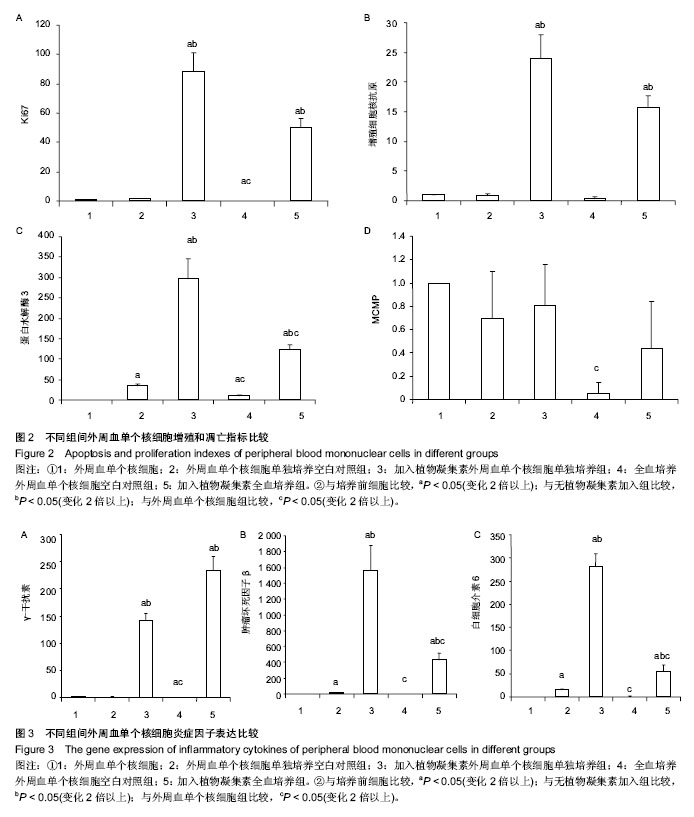
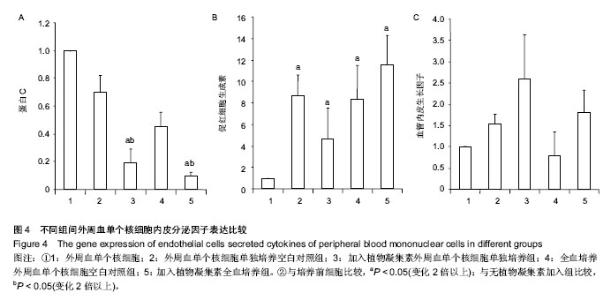
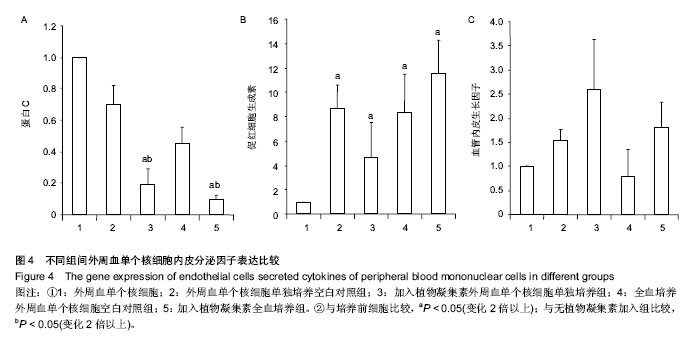
2.4 植物凝集素促进外周血单个核细胞免疫类细胞因子表达 选取免疫调节中重要的分泌类细胞因子(γ-干扰素、肿瘤坏死因子β和白细胞介素6)进行荧光半定量测定,检测不同的体外培养和植物凝集素的加入对其基因表达的影响(表3)。 所有的免疫类分泌因子,植物凝集素加入组对比空白组和培养前外周血单个核细胞都有明显升高(P < 0.05)。全血培养组(不含植物凝集素)γ-干扰素表达量较培养前和外周血单个核细胞单独培养有明显下降(P < 0.05)。 肿瘤坏死因子β和白细胞介素6变化较一致:①全血培养组(不含植物凝集素)与培养前外周血单个核细胞比较变化不明显,单纯外周血单个核细胞培养组较两者有明显升高。②含植物凝集素的外周血单个核细胞单纯培养组较含植物凝集素的全血培养组表达量明显升高(图3)。 2.5 体外培养及植物凝集素对内皮类因子表达的影响 因外周血中可以分离、培养内皮细胞,而内皮细胞是凝血的重要靶细胞。为检测体外培养和植物凝集素的加入对内皮细胞的影响,对内皮(或者凝血)类重要的分泌类细胞因子(血管内皮生长因子、促红细胞生成素和蛋白C)进行荧光半定量测定(表1)。 发现血管内皮生长因子和促红细胞生成素的表达量在加入植物凝集素培养后有所升高,血管内皮生长因子变化不明显(P > 0.05),而促红细胞生成素变化差异有显著性意义。蛋白 C的表达在加入植物凝集素培养后有明显下降 (P < 0.05),见图4。"
| [1] 许树成.人微量全血培养与染色体标本制作技术研究[J].生物学杂志, 2005,22(4):46-47.
[2] 谭雷涛,王凌燕,常维山,等.全血培养与酶标仪联用检测淋巴细胞转化的研究[J].中国农学通报,2006,22(1): 1-3.
[3] Tsai WJ, Chen YC, Wu MH, et al. Seselin from Plumbago zeylanica inhibits phytohemagglutinin (PHA)-stimulated cell proliferation in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Ethnopharmacol.2008; 119(1):67-73.
[4] Katiyar S, Awasthi SK, Sahu RK. Suppression of IL-6 level in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells stimulated with PHA/LPS after occupational exposure to chromium. Sci Total Environ. 2008; 390(2-3):355-361.
[5] Lei P, He Y, Ye Q, et al. Antigen-binding characteristics of AbCD71 and its inhibitory effect on PHA-induced lymphoproliferation. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica. 2007; 28(10):1659-1664.
[6] Ide K, Momoi Y, Iwasaki T. Canine PHA-stimulated adherent cell enhance interferon-gamma production and proliferation of autologous peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Vet Comp Oncol. 2005; 3(1):25-31.
[7] 王悦.人全血培养方法筛选抗类风湿性关节炎青藤碱衍生物[J]. 中国实用医药, 2013, 8(30):255.
[8] Janefjord CK, Jenmalm MC. PHA-induced IL-12R beta(2) mRNA expression in atopic and non-atopic children. Clin Exp Allergy. 2001;31(10):1493-1500.
[9] Dabrowski MP, Stankiewicz W, Plusa T, et al. Competition of IL-1 and IL-1ra determines lymphocyte response to delayed stimulation with PHA. Mediators of inflammation. 2001; 10(3): 101-107.
[10] Chen YC, Chang SC, Wu MH, et al. Norcantharidin reduced cyclins and cytokines production in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Life Sci. 2009;84(7-8):218-226.
[11] Javadian A, Salehi E, Bidad K,et al. Effect of Estrogen on Th1, Th2 and Th17 Cytokines Production by Proteolipid Protein and PHA Activated Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells Isolated from Multiple Sclerosis Patients. Arch Med Res. 2014; 45(2):177-182.
[12] Valor L, Sarmiento E, Navarro J, et al. Evaluation of lymphoproliferative responses by carboxy fluorescein succinimidyl ester assay in heart recipients with infections. Transplant Proc. 2012; 44(9):2649-2652.
[13] Scavella A, Leiva L, Monjure H, et al. Effect of L-arginine supplementation on immune responsiveness in patients with sickle cell disease. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2010; 55(2): 318-323.
[14] Meier V, Burger E, Mihm S, et al. Ribavirin inhibits DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis in PHA-stimulated human peripheral blood mononuclear cells: possible explanation for therapeutic efficacy in patients with chronic HCV infection. J Med Virol. 2003; 69(1):50-58.
[15] Morgan R, Chen Z, Richkind K, et al. PHA/IL2: an efficient mitogen cocktail for cytogenetic studies of non-Hodgkin lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer Geneti Cytogenet. 1999; 109(2):134-137.
[16] Martin-Ramirez J, Hofman M, van den Biggelaar M, et al. Establishment of outgrowth endothelial cells from peripheral blood. Nat Protocol. 2012; 7(9):1709-1715.
[17] Estes ML, Mund JA, Ingram DA, et al. Identification of endothelial cells and progenitor cell subsets in human peripheral blood.Curr Protoc Cytom. 2010;Chapter 9:Unit 9.33.1-11.
[18] Fidan I, Yesilyurt E, Kalkanci A, et al. Immunomodulatory Effects of Voriconazole and Caspofungin on Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells Stimulated by Candida albicans and Candida krusei. Am J Med Sci. 2014.
[19] Bellik L, Musilli C, Vinci MC, et al. Human mature endothelial cells modulate peripheral blood mononuclear cell differentiation toward an endothelial phenotype. Exp Cell Res. 2008;314(16):2965-2974.
[20] MacCarthy EP, Ooi YM, Hsu A, et al. Evidence for an endothelial cell-derived factor which stimulates the growth of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Cell Immunol. 1985;91(2):492-497.
[21] Ulmer AJ, Scholz W, Ernst M, et al. Response of human T lymphocytes to phytohemagglutinin (PHA) after sequential depletion of monocytes, HLA-DR+, Leu11a+, and Leu7+ cells. Immunobiology. 1985;170(5):419-433.
[22] Luquetti A, Janossy G. Lymphocyte activation. VIII. The application of a whole blood test to the quantitative analysis of PHA responsive T cells. J Immunol Methods. 1976; 10(1): 7-25.
[23] Scappaticci S, Danesino C, Rossi E, et al. Cytogenetic abnormalities in PHA-stimulated lymphocytes from patients with Langerhans cell histocytosis. AIEOP-Istiocitosi Group. Br J Haematol. 2000;111(1):258-262.
[24] Vermaelen K, Barbieri D, Van den Berghe H. Indirect stimulation of B-cell proliferation in vitro by T cells, as evidenced by cytogenetic analysis of PHA-stimulated cell cultures of B-cell lymphomas. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1984; 11(4):425-428.
[25] Zhang Z, Ding Y, Li W, et al. Interleukin-17A- or tumor necrosis factor alpha-mediated increase in proliferation of T cells cocultured with synovium-derived mesenchymal stem cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013;15(5): R169.
[26] Ribeiro A, Laranjeira P, Mendes S, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells from umbilical cord matrix, adipose tissue and bone marrow exhibit different capability to suppress peripheral blood B, natural killer and T cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013;4(5):125.
[27] Gupta D, Rani M, Khan N, et al. HIV-1 Infected Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells Modulate the Fibrogenic Activity of Hepatic Stellate Cells through Secreted TGF-beta and JNK Signaling. PloS one. 2014;9(3):e91569.
[28] Glantz Y, Sabag O, Lichtenstein M, et al. Eliminating the six N-terminal amino acids of the caspase 3 large subunit improved production of a biologically active IL2-Caspase3 chimeric protein. Biotechnol Prog. 2012;28(2):573-580.
[29] Shing CM, Peake JM, Suzuki K, et al. Bovine colostrum modulates cytokine production in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells stimulated with lipopolysaccharide and phytohemagglutinin. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2009;29(1): 37-44.
[30] Vongsakul M, Aksomboon A. Cyclins D1, E, A expression and synergistic cytotoxicity to a cholangiocarcinoma cell line from recombinant TNF-alpha and PHA supernate. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2002;20(1):57-60.
[31] Eichmann A, Simons M. VEGF signaling inside vascular endothelial cells and beyond. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2012; 24(2): 188-193.
[32] Trincavelli ML, Da Pozzo E, Ciampi O, et al. Regulation of Erythropoietin Receptor Activity in Endothelial Cells by Different Erythropoietin (EPO) Derivatives: An in Vitro Study. Int J Molecular Sci. 2013;14(2):2258-2281.
[33] Castellino FJ, Ploplis VA. The protein C pathway and pathologic processes. J Thromb Haemost. 2009;7 Suppl 1:140-145. |
| [1] | Xi Li-cheng, Li Hong-yu. Research progress of the influence of alcohol on the local microenvironment of femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1137-1142. |
| [2] | Wang Jian-ji, Yang Long, Li Jing, Sun Qi, Zuo Wei-min, Ren Qi-feng, Sun Yu, Wu Zhan-yu, Zou Qiang, Ma Min-xian, Ye Chuan. Development and application of special-purpose grafter by femoral head decompression combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells transplantation based on three-dimensional printing technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(44): 6636-6642. |
| [3] | Zhou Chang-yan, Zhou Qing-huan, Bian Jing, Chen Ke, Chen Wen. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells combined with calcium phosphate cement to repair articular cartilage defects in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(8): 1195-1199. |
| [4] | Xu Xiang, Yin He-ping. Platelet-rich plasma accelerates the proliferation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2144-2148. |
| [5] | Ma Fa-ku, Wang Huan, Liu Bin, Yang Yan-li, Su Qin-jun, Qian Zhen, Dong Liang. Expression of CD44+/C-myc+ cancer stem cells and its relationship with the prognosis of patients in colorectal tumors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2161-2166. |
| [6] |
Chen Ping, Wang Jian.
Enrichment of lung cancer stem cells and expression of related markers
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2167-2171.
|
| [7] | Fan Zhi-gang, Fan Hong-liang. Oxidative stress response in diabetic nephropathy rats following injection of embryonic stem cells via the tail vein [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2199-2204. |
| [8] | Zhao Xiao-jian, Lu Cai-ping, Chu Wei-wei, Zhang Ya-xiao, Zhang Bing, Zhen Qiang, Tan Guo-liang, Wang Ren-feng, Liu Jia-bao, Wu Lin. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for treatment of emphysema: intravenous versus intratracheal approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2211-2215. |
| [9] | Wang Yong, Zhao Wei, Feng Jian-zhou, Chen Xiao-chun. Nerve growth factor-modified adipose derived stem cells for repair of spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2224-2229. |
| [10] | Sha Wen-qiong, She Rui-lian, Wang Zi-neng, Ke Ru. Ultrastructure and phagocytotic function of human placental mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2230-2235. |
| [11] | Du Qing-hua, Cao Jun-kai, Dong Xi-xi, E Ling-ling, Wei Li-jun. Osteogenic differentiation of pluripotent stem cells induced by akermanite extracts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2236-2242. |
| [12] | Wu Yan, Huang Lan . Bone morphogenetic protein 9-induced osteogenic differentiation of dental follicle cells in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2255-2260. |
| [13] | Rao Li-jia, Li Qi-meng, Li Jin-ling, Xu Qiong. Expression pattern of ten-eleven translocation family during differentiation of human dental pulp cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2261-2266. |
| [14] | Gao Zhuo-yue, Liu Yong-qi, He Jian-xin, Wu Zhi-wei, Luo Ya-li, Su Yun, Zhang Li-ying, Zhang Qi, Wu You-ming, Zhou Ni-na. Regulatory effects of warming yang and invigorating qi treatment on the inflammatory balance and genetic stability of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells under tumor microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2267-2272. |
| [15] | Wang Fang, Chen Shao-wei. In vitro culture of embryos and establishment of embryonic stem cell lines [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2273-2277. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||